Fibroids may cause the following symptoms:
- Changes in menstruation
- Longer, more frequent, or heavy menstrual periods
- Menstrual pain (cramps)Painful periods
- Vaginal bleeding at times other than menstruation
- Anemia (from blood loss)
- Pain
- In the abdomen or lower back (often dull, heavy and aching, but may be sharp)
- During sex
- Pressure
- Difficulty urinating or frequent urination
- Constipation, rectal pain, or difficult bowel movements
- Abdominal cramps
- Enlarged uterus and abdomen
- Miscarriages
- Infertility
These symptoms also may be signs of other problems. Therefore, you should see your doctor if you have any of these symptoms.
Fibroids also may cause no symptoms at all. Fibroids may be found during a routine pelvic exam or during tests for other problems.
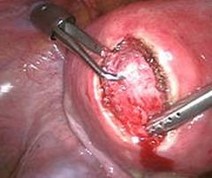
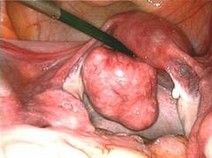
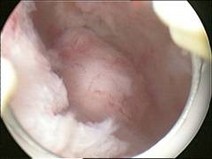
Growth and location are the main factors that determine if a fibroid leads to symptoms and problems. A small lesion can be symptomatic if located within the uterine cavity while a large lesion on the outside of the uterus may go unnoticed. Different locations are classified as follows:
- Intramural fibroids are located within the wall of the uterus and are the most common type; unless large, they may be asymptomatic.
- Subserosal fibroids are located underneath the mucosal (peritoneal) s u rface of the uterus and can become very large. They can also grow out in a papillary manner to become pedunculated fibroids. These pedunculated growths can actually detach from the uterus to become a parasitic leiomyoma.
- Submucosal fibroids are located in the muscle beneath the endometrium of the uterus and distort the uterine cavity; even small lesion in this location may lead to bleeding and infertility. A pedunculated lesion within the cavity is termed an intracavitary fibroid and can be passed through the cervix.
- Cervical fibroids are located in the wall of the cervix (neck of the uterus). Rarely fibroids are found in the supporting structures (round ligament, broad ligament, or uterosacral ligament) of the uterus that also contain smooth muscle tissue.